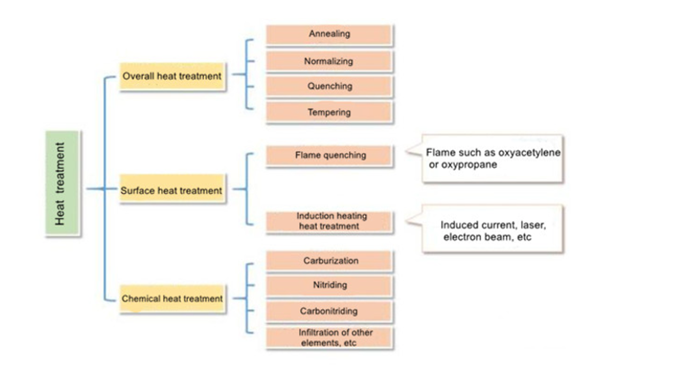
Heat treatment is a controlled process used to alter the physical and sometimes chemical properties of materials, particularly metals and alloys, to achieve desired characteristics such as increased strength, hardness, or ductility. The validation of the heat treatment process ensures that the process consistently produces results that meet predetermined specifications and quality standards. This is a critical step in industries like aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing, where material performance is vital.
Key Components of Heat Treatment Validation
Understanding Material Requirements:
The first step in validation is understanding the specific requirements of the material being treated. For example, certain alloys may need precise temperature ranges or controlled cooling rates to achieve desired properties. A detailed review of material specifications, mechanical properties, and metallurgical requirements is essential.
- Establishing Process Parameters:
Validation involves defining critical process parameters such as heating temperature, soaking time, cooling methods, and quenching mediums. These parameters must align with industry standards (e.g., AMS 2750 for aerospace) or specific client requirements. - Calibration of Equipment:
The heat treatment equipment, including furnaces, thermocouples, and controllers, must be calibrated to ensure accuracy and repeatability. Regular equipment maintenance and adherence to calibration schedules are crucial to prevent deviations. - Performing Trial Runs:
Before the process is finalized, trial runs are conducted using sample materials. These samples are then tested for properties such as hardness, tensile strength, or microstructure to confirm that the process produces the desired outcomes. - Testing and Inspection:
Non-destructive testing (NDT) methods such as ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle inspection, or dye penetrant testing are often employed to validate the absence of defects. Destructive testing, like tensile or impact testing, may also be used to verify mechanical properties. - Documentation and Records:
Validation includes maintaining detailed records of each heat treatment cycle. Documentation should include process parameters, equipment calibration data, and inspection reports to provide traceability and accountability. - Ongoing Monitoring and Revalidation:
Validation is not a one-time process. Regular monitoring ensures the heat treatment process remains consistent over time. Revalidation is performed when there are significant changes in equipment, materials, or process parameters.
Importance of Heat Treatment Validation
Validation ensures that materials perform as expected under operational conditions, reducing the risk of failures. For critical applications, such as aircraft components or medical implants, even minor deviations in material properties can lead to catastrophic consequences. A validated heat treatment process minimizes variability, increases product reliability, and ensures compliance with regulatory and customer requirements.
The validation of the heat treatment process is a systematic approach that guarantees material quality and reliability. By defining and controlling key parameters, calibrating equipment, and conducting thorough inspections, manufacturers can achieve consistent and repeatable results, meeting both industry standards and customer expectations. This rigorous process not only enhances product performance but also builds confidence in the supply chain.
Post time: Dec-13-2024